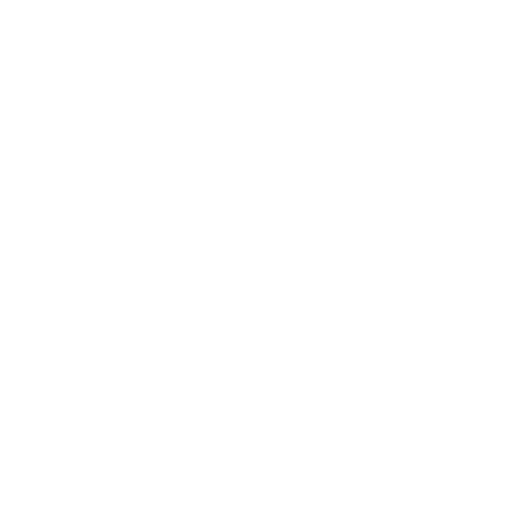
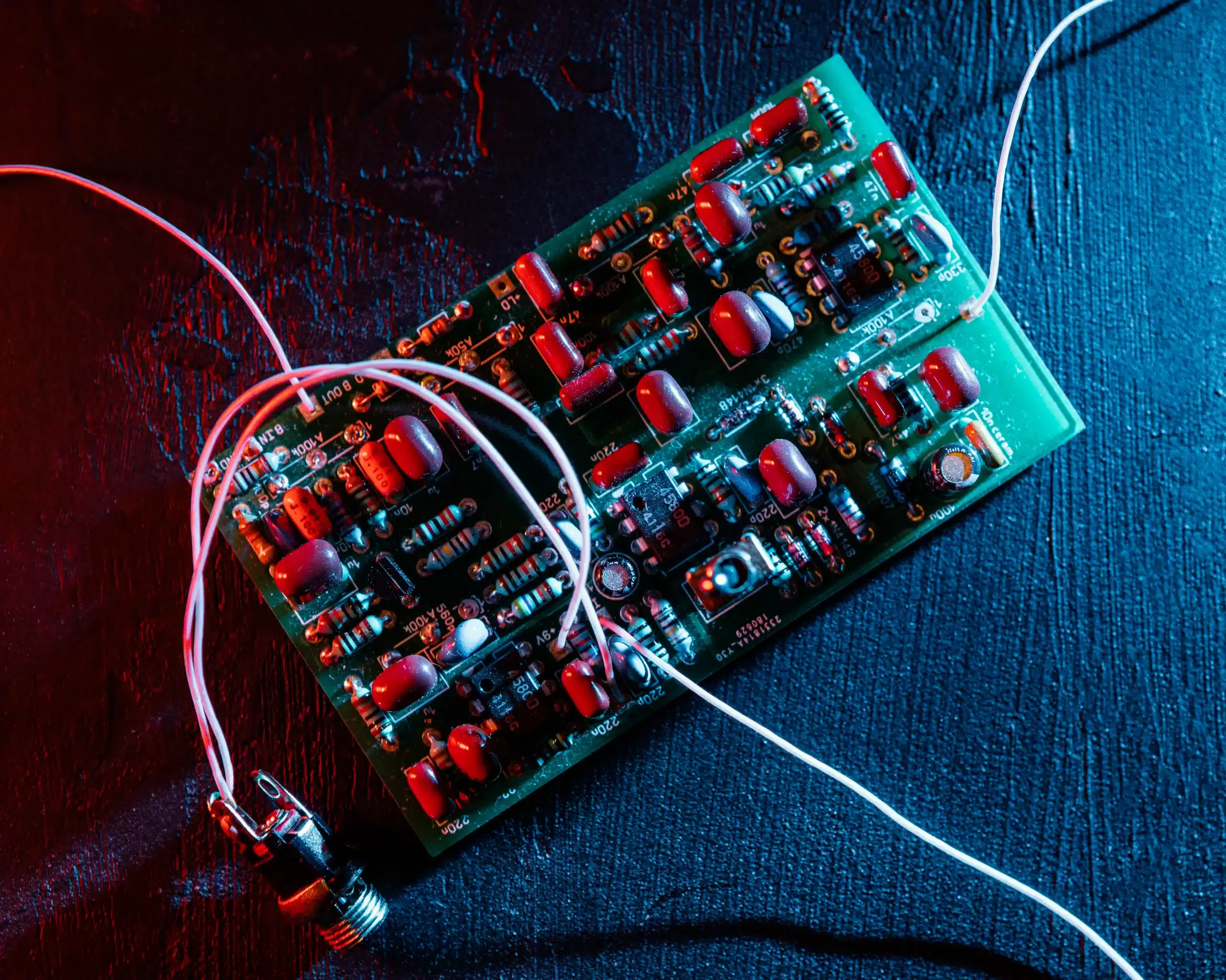
Electronic components form the backbone of every modern device—from smartphones and televisions to home appliances and even medical equipment. Whether you are a student, hobbyist, or beginner in electronics, understanding the basic building blocks of circuits is essential. This guide will walk you through the fundamentals of electronic components, their types, and their real-world applications, making electronics less intimidating and more approachable.
A Beginner’s Guide to the 5 Basic Components of an Electronic Circuit
Electronic circuits rely on a handful of basic components. Let’s explore the five essential ones:
1. Resistors
Resistors control the flow of current in a circuit. They are often used to limit the current going to delicate parts, such as LEDs.
Example: In a torchlight, resistors prevent the LED bulb from burning out due to excess current.

2. Capacitors
Capacitors store and release electrical energy. They are widely used in devices requiring temporary power storage.
Example: Camera flashes use capacitors to quickly release stored energy, producing a burst of light.

3. Inductors
Inductors store energy in magnetic fields and oppose changes in current flow.
Example: In radio receivers, inductors help tune frequencies, enabling the device to capture specific signals.

4. Diodes
Diodes allow current to flow in only one direction, acting as gatekeepers of electricity.
Example: Phone chargers use diodes to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC).

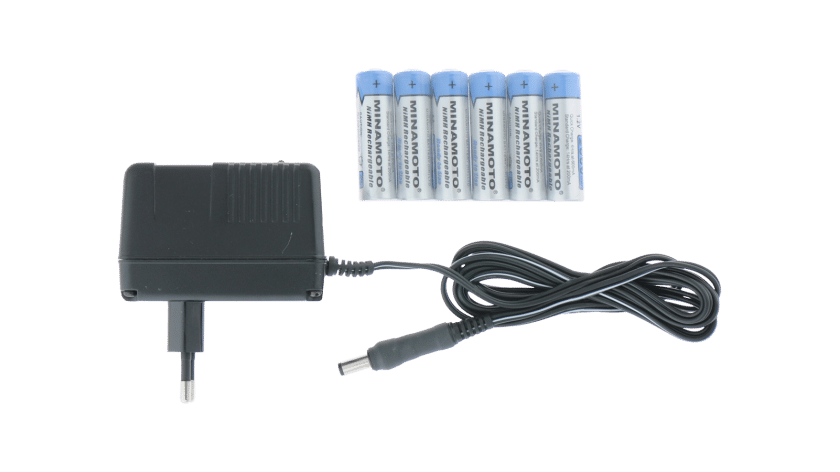
5. Power Sources
No circuit can function without a power supply. Batteries or power adapters serve as the energy source for circuits.
Example: A TV remote is powered by AA batteries, which provide the necessary voltage for operation.
Passive vs. Active: Understanding the Two Main Types of Electronic Components
Electronic components are broadly divided into two categories: passive and active.
Passive Components
- Do not generate energy; they only consume or store it.
- Examples: resistors, capacitors, inductors.
Real-life example: The capacitor inside a ceiling fan helps regulate speed but doesn’t generate energy.
Active Components
- Can control current flow and even amplify signals.
- Examples: transistors, integrated circuits (ICs), diodes.
Real-life example: A transistor in a microphone amplifier boosts the weak voice signal so listeners hear it clearly.
Everything You Need to Know About Electronic Circuits: Types and Components
Series Circuits
In series circuits, components are connected end-to-end, so the same current flows through all.
Example: Old Christmas lights where one faulty bulb caused the whole string to stop working.
Parallel Circuits
In parallel circuits, components are connected across the same voltage source. If one fails, others continue to work.
Example: Modern home wiring ensures lights and fans work independently.
Mixed (Combination) Circuits
These use both series and parallel arrangements to balance reliability and functionality.
Example: Household appliances like washing machines use mixed circuits for different functions.
What’s the Difference Between Electrical and Electronic Components?
Electrical and electronic components are often confused, but they are not the same.
- Electrical Components: Handle large amounts of current and power (e.g., switches, motors, wires).
- Electronic Components: Work with smaller signals, controlling or processing them (e.g., resistors, transistors, ICs).
Example Comparison:
- A ceiling fan (electrical component) simply converts electrical energy into motion.
- A remote-controlled fan (electronic components) processes signals to adjust speed wirelessly.
From Resistors to Transistors: A Glossary of Essential Electronic Components
Here’s a quick glossary for beginners:
- Resistor – Limits current flow.
- Capacitor – Stores and releases energy.
- Inductor – Manages magnetic energy.
- Diode – Allows one-way current flow.
- Transistor – Switches or amplifies signals.
- LED – Light-emitting diode used in displays and indicators.
- Relay – Electrically operated switch.
- IC (Integrated Circuit) – A “mini-circuit” containing multiple components.
- Transformer – Steps voltage up or down.
Conclusion
Understanding electronic components is the first step toward mastering electronics. Whether you’re working on a school project, repairing gadgets, or beginning your DIY electronics journey, these building blocks will be essential.